At some point in most people’s lives, usually after a really good rock concert, it’s common to wonder if hearing loss can be reversed. The ability to hear is often unappreciated until it starts to fade. However, losing your hearing doesn’t always mean it’s gone for good.
Key Takeaways: Reversing Hearing Loss
- There are three types of hearing loss: sensorineural, conductive, and mixed.
- Sensorineural involves damage to the auditory nerve.
- Conductive loss usually involves a physical obstruction.
- Sensorineural hearing loss usually can’t be reversed, while conductive often can be.
- Treatments can include hearing aids, cochlear implants, and others.
- There are some alternative treatments for hearing loss, but they may not be effective on their own.
What Are the Different Causes of Hearing Loss?
The process of hearing begins when your outer ear interacts with sound waves, collected in your ear canal. The middle ear includes bones that vibrate in reaction to the sound, so that nerves in the inner ear can sense the vibration and transmit a signal to the brain. If part of that process is obstructed, you may begin to have trouble hearing.
Causes of hearing loss include:
- Aging.
- Noise exposure.
- Illness, including ear infections.
- Some medications.
- Physical injury.
- Genetics [1].
Sudden hearing loss can be a sign of damage to the ear. In children, it’s common to develop other communication disorders. Hearing-impaired seniors are more likely to develop dementia, as well [2].
If you aren’t sure, some of the best online hearing tests can help you decide if it’s worth seeing a doctor. Signs of hearing loss include:
- Sounds seem muffled.
- Difficulty with high-pitched noises.
- Difficulty hearing with background noise.
- Asking others to speak more slowly or loudly.
- Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears [3].
What percentage of people aged 75 and over have disabling hearing loss?

What Are the Different Types of Hearing Loss?
There are three types of hearing loss, including:
- Sensorineural hearing loss.
- Conductive hearing loss.
- Mixed hearing loss [4].
Each type of hearing loss tends to affect hearing in a similar way, at first seeming almost to muffle sound. At that point, it’s a good idea to check our ear health.
Sensorineural
Sensorineural hearing loss has its origin either in the auditory nerve or the hair cells where vibration is detected. If those are damaged, electrical impulses are interfered with. In the case of complete deafness, they may be stopped entirely.
Sensorineural is the most common type of permanent hearing loss. Age-related hearing loss and noise-induced hearing loss are usually of this type. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss is usually the result of damage to the inner ears.
Conductive
Conductive hearing loss is the result of a physical obstruction or trauma, usually in the middle or outer ears. Common causes of conductive hearing loss include osteoporosis in the small bones of the middle ear, earwax buildup in the outer ear, or even a foreign object. Damage due to ear infections is another cause.
Mixed
As you might expect, mixed hearing loss is a combination of both other types. It involves both a physical obstruction and interference with electrical impulses.
Can Hearing Loss Be Reversed?
Restoring hearing is achievable in some cases, though it depends on the causes of the hearing loss. Reversing sensorineural hearing loss is usually not possible. Older folks may be stuck with age-related hearing loss. Damage to the ear may also cause irreversible hearing loss.
It is possible in many cases to reverse hearing loss that is conductive in nature. Hearing loss treatment in those cases may involve surgery or medicine.
Treating Sensorineural Hearing Loss
In most cases, this type of hearing loss can’t be cured in the sense of hearing loss reversal. It is unfortunately permanent, as most cases involve damage to nerve cells. However, such a diagnosis does not doom you to eventual deafness.
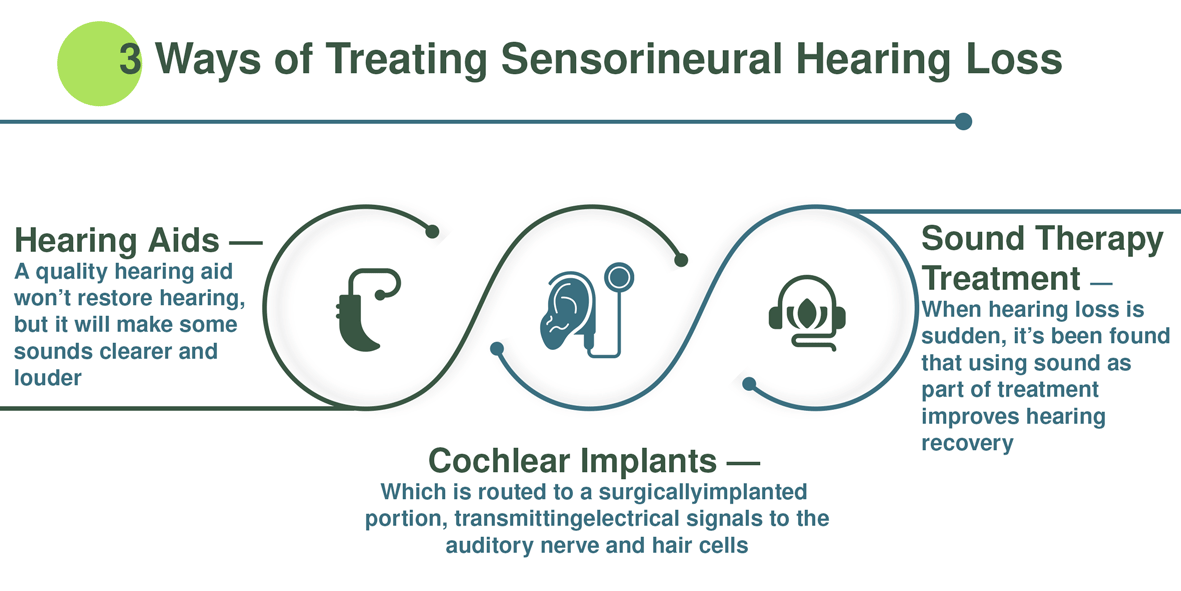
Hearing Aids
A hearing aid is one of the most common ways of addressing hearing loss, particularly sensorineural hearing loss. A quality hearing aid like the MDHearingAid VOLT+ won’t restore hearing, but instead, it will make some sounds clearer and louder.
Cochlear Implants
Cochlear implants are another option when your hearing health isn’t great. In some ways, it’s a device similar to a hearing aid. A microphone sits behind the ear and picks up sounds. From there, it is routed to a surgically implanted portion that transmits electrical signals to the auditory nerve and hair cells, basically replacing the outer and middle ear [5].
Sound Therapy Treatment
When hearing loss is sudden, it’s been found that using sound as part of treatment improves hearing recovery. The mechanism is still being explored, but it might have something to do with retraining sensory nerves [6].
Treating Conductive Hearing Loss
Reversing conductive hearing loss is more likely. However, it may not always be an option. Treatment options may include surgery or medicine, though sufferers are often treated with both.
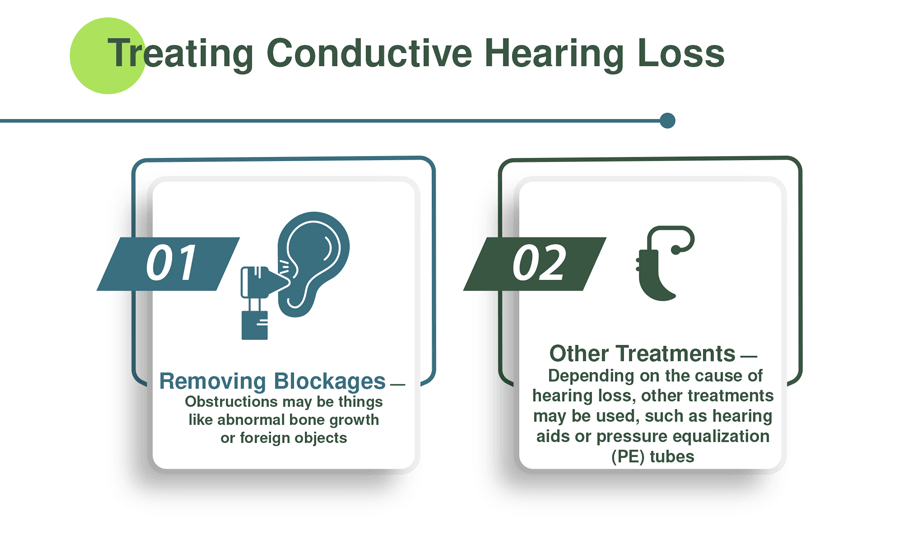
Removing Blockages
The small bones in the middle ear called ossicles need to be able to vibrate in order to transmit sound. An obstruction can prevent that or other aspects of the hearing process. Removing the obstruction usually restores hearing.
Obstructions may be things like abnormal bone growth or foreign objects.
Other Treatments
Depending on the cause of hearing loss, other treatments may be used. For example, while hearing loss due to infections can’t be reversed, using pressure equalization (PE) tubes helps improve ear health. Hearing aids are also an option.
Treating Mixed Hearing Loss
As it combines both varieties of hearing loss, addressing mixed hearing loss can require several different types of treatment. Surgery, medicine, or a hearing aid may be necessary.
Alternative Ways of Reversing Hearing Loss
There may be more sufferers of hearing loss that don’t seek treatment than do. It’s not surprising, therefore, that some home treatments have become popular. Ear candles, for example, may help with ear wax. Other approaches include:
- Ginkgo biloba extract.
- Ginger tea.
- Tea tree oil.
- Cajeput essential oil.
- Lifestyle changes.
Alternative treatments are probably limited in what they can address. However, some may provide some degree of relief. Just remember to check with your doctor first.
Ginkgo Biloba Extract
There’s some evidence that ginkgo can help treat hearing loss. When combined with medicine and other treatments, it helped those suffering from sudden hearing loss to regain it to a greater degree. The evidence isn’t conclusive as yet, however [7].
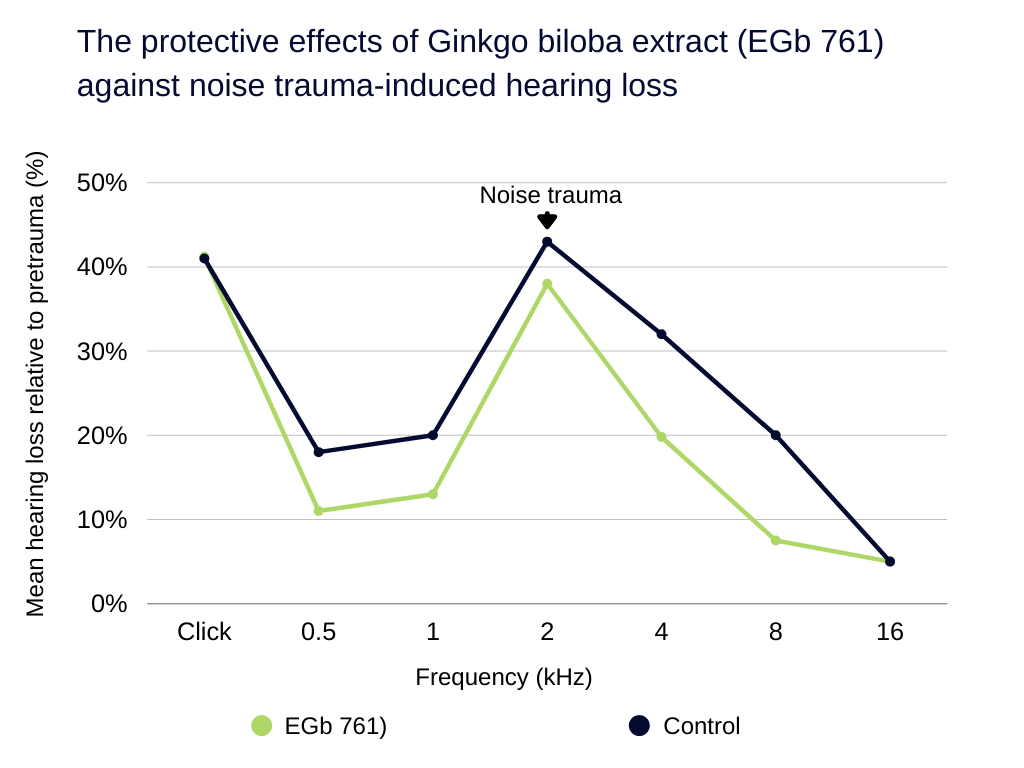
Source:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4083883/
Ginger Tea
There is some indication that antioxidants may prevent damage to nerves long term [8]. As a result, age-related hearing loss is reduced. Ginger is packed full of antioxidants, so it’s possible it may help to some degree.
Tea Tree Oil
Often used as a less harsh, natural antiseptic, tea tree oil might also be useful to prevent ear infections. However, it’s generally only recommended for external use.
Cajeput Essential Oil
Like tea tree oil, cajeput oil may be useful as an antibacterial to prevent infections. Though like tea tree oil, caution might be wise [9].
Lifestyle Changes
Hearing and ear health are part of general health. Exercise and diet keep your body in better shape so you’re better able to resist infections and damage, and recover faster. Avoiding loud noises and wearing ear protection in noisy areas is also a good idea.
FAQ
You probably are wondering about one of these frequently asked questions. We can help.
Can My Hearing Loss Be Reversed?
That may be a question only your doctor can answer. It will probably depend on the cause of the hearing loss. If there is an obstruction in your outer or middle ear, it may be possible. If the damage is to nerves in the inner ear, you may be stuck with it.
Are There Any Drugs That Fix Hearing Loss?
At present, there aren’t any drugs that directly address hearing loss. Some types of medicine that can address the causes of hearing loss. For example, osteoporosis in the ossicles might be addressed with a prescription.
What Is the Most Common Cause of Noise Induced Hearing Loss?
Some of the most common causes include:
- Occupational noise.
- Loud music.
- Loud machinery [10].
What Is the Future of Hearing Loss Reversal?
Much of current research focuses on sensorineural loss and ways of addressing it. Approaches include gene therapy and stem cell research to treat nerve damage.
Conclusion
A certain amount of hearing loss may be inevitable as we age. However, there is plenty that we can do to preserve our ability to hear. Even when some sounds fade, it may be possible to turn the volume back up.
References:
- “Causes of Hearing Loss in Adults.” American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, https://www.asha.org/public/hearing/causes-of-hearing-loss-in-adults/.
- Brodie, Arjuna, et al. “The Impact of Rehabilitation on Quality of Life after Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review.” European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 23 Aug. 2018, https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00405-018-5100-7.
- “How Do I Know If I Have Hearing Loss Caused by Loud Noise?” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 24 Aug. 2021, https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/hearing_loss/how_do_i_know_if_i_have_hearing_loss.html
- “Types of Hearing Loss.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 8 June 2020, https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/hearingloss/types.html.
- “Hearing Loss Treatment and Intervention Services.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 8 June 2020, https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/hearingloss/treatment.html.
- Lopez-Gonzalez, Miguel A, et al. “[Sound Therapy in Sudden Deafness].” Acta Otorrinolaringologica Espanola, U.S. National Library of Medicine, May 2012, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22152653/.
- Si, Xia, et al. “Efficacy and Safety of Standardized Ginkgo Biloba L. Leaves Extract as an Adjuvant Therapy for Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” Journal of Ethnopharmacology, Elsevier, 30 Aug. 2021, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378874121008163.
- Fujimoto, Chisato, and Tatsuya Yamasoba. “Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants for Treatment of Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review.” MDPI, Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute, 24 Apr. 2019, https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3921/8/4/109/htm.
- Jedlickova, Z, et al. “Antibacterial Properties of the Vietnamese Cajeput Oil and Ocimum Oil in Combination with Antibacterial Agents.” Journal of Hygiene, Epidemiology, Microbiology, and Immunology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 1992, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1293213/.
- “Causes of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss.” Stanford Health Care (SHC) – Stanford Medical Center, 1 Aug. 2018, https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-conditions/ear-nose-and-throat/noise-induced-hearing-loss/causes.html.

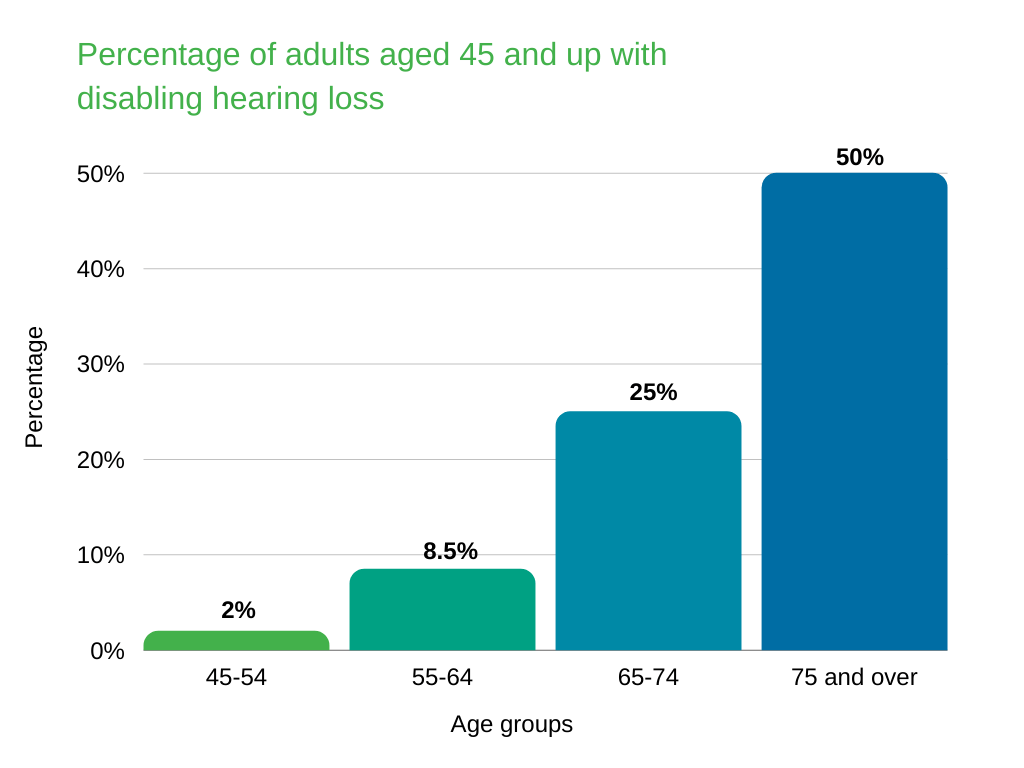




Leave a Reply